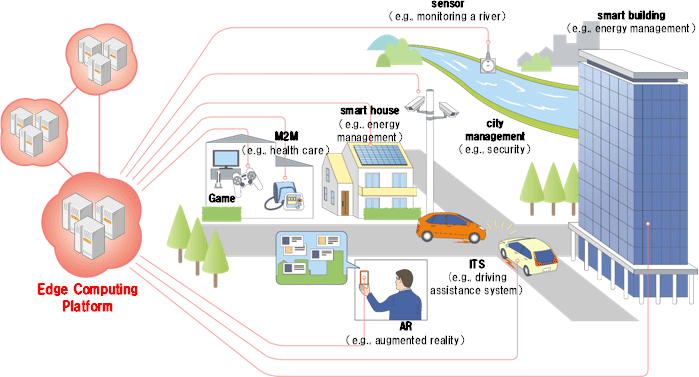
The high pace of urbanization has led to the need for faster, smarter, and more efficient solutions to technology. The cities are becoming digitalized, where systems based on data operate transportation, energy, safety, and healthcare. One of these technologies is smart cities, which is experiencing tremendous demand. Edge computing guarantees speed, reliability, and improved decision-making by performing computation nearer to the source, instead of depending on remote cloud servers, as in the case of modern cities. In this article, we are going to have a look at six incredible aspects that bring edge computing to the success of smart cities.
- Real-Time Data Processing
Real-time data processing is one of the strongest aspects of Smart cities edge computing. Old systems are usually characterized by delays in transferring information to the cloud. Edge computing allows analysis, however, immediately at the point of data collection or close to it. This is essential in applications such as traffic management characterized management, where a delay as short as several seconds may create a congestimanagement, congestion or even an accident. Real-time processing allows one to save lives and become more efficient due to the ability to gain immediate insights and take appropriate actions in difficult situations.
- Reduced Network Latency
Smart city services can have a significant impediment due to network delays. Edge computing addresses the issue by minimizing congestion and latency due to local data management. To demonstrate, self-motivated vehicles as well as computer-controlled traffic lights will demand responses in microseconds. The use of smart cities makes these systems work instantly, minimizing instantly, making cities safer and effiinstantly, and morecient. Reduced latency can also improve the experience of users taking services like Wi-Fi in the city or digital kiosks and mobile payments, which are slowly becoming a part of urban life.
- Greater Security and Privacy.
Security is one of the leading issues in urban areas where millions of people are dependent on interconnected systems Edge computing eliminates risks because sensitive data is stored nearer. Not all the information is transferred to centralised servers, but only the necessary information is exchanged. This decreases the possibility of massive breaches and improves data privacy. To illustrate, smart healthcare gadgets in a metropolis could work with patient information on-site and only transmit the applicable notices to the centralized systems. Accessibility and protection are crucial attributes of contemporary cities.
- Scalability and Flexibility.
The smart cities are ever-expanding, and their technological requirements keep changing. Edge computing offers scalability and flexibility, and it suggests that cities do not have to redesign their existing infrastructures to expand them. In the modular implementation of edge computing nodes, a number of nodes can be added in the form of sensors, devices, or networks. Whether it is in terms of the support of thousands of surveillance cameras or newly developed IoT applications, scalability ensures that a city can comfortably expand to whatever it needs without such drastic shocks in the future.
- Energy Saving and Sustainability.
Smart city development is based on the concept of sustainability. One way of achieving this is through edge computing, which offers more energy efficiency. Localised process minimizes power consumption instead of moving huge quantities of data over great distances. As an example, the smart grids could be used to optimize and minimise the power consumption by processing the energy data on site and adjusting the power consumption in real time. This not only saves energy but also the expenditure of governments and citizens. Edge computing can help directly improve the environmental footprint of city living by making it greener and more sustainable.
- Improved Citizen Services
The last characteristic that makes smart cities computing impressive is that it enhances services to citizens. Edge computing offers timely and accurate information in the form of smart parking solutions as well as real-time updates the transport. Reductions in waiting time, improved resource distribution, and safer environments are benefiting the citizens. To illustrate, edge computing-powered emergency response systems can identify the incident and send alerts to the responders in a few seconds. This direct enhancement in daily living makes people have confidence in their city governments.
(FAQs)
Q1: What does edge computing have to do with smart cities?
The smart cities are enabled by edge computing to handle the data nearer to its origin, which means quicker response, enhanced privacy, and enhanced cities’ efficiency.
Q2: What are the benefits of smart cities edge computing to safety?
It sustains systems such as traffic control, emergency response, and surveillance through latency and provides real-time actions.
Q3: Can edge computing be cost-effective for cities?
It does save on energy expenses, it lowers the overloading of infrastructure, and it enables gradual growth, which makes it an economical solution.
Q4: Does edge computing allow supporting sustainability objectives?
Absolutely. Edge computing contributes specifically to the greener city initiatives by minimizing data transfers and resource wastage.
Q5: What are the real-life examples of the use of edge computing in cities?
Smart grids, intelligent traffic lights, connected healthcare systems, and smart waste management are a few of the applications.
Conclusion
The cities are transforming the way they work with smart cities and edge computing. Edge computing helps to make cities more intelligent and sustainable, and provides real-time data processing and decreases in latency, as well as higher data privacy and energy efficiency. It is a vital component of modern urban evolution because it is a scalable tool that can be utilised to advance the services to the citizens. These six amazing features make edge computing not just a technological enhancement; it is a platform over which to build safer, greener, more responsive services to the needs of their citizens.